AI in social media is revolutionizing how influencers engage with audiences, offering personalized content and insights that drive deeper connections across platforms. But, in the evolving world of social media, a new type of influencer has emerged — one that doesn’t eat, sleep, or exist in the traditional sense. AI influencers, also known as virtual influencers, are digitally-created personas powered by artificial intelligence, designed to engage audiences just like their human counterparts.
These virtual personalities, such as Lil Miquela, Shudu, have amassed millions of followers, signed brand deals, and blurred the lines between reality and fiction. As technology advances and AI becomes more integrated into everyday life, understanding AI influencers is essential for anyone interested in the future of marketing, social media, and digital innovation.
What Are AI Influencers?
AI influencers, also known as virtual influencers, are computer-generated characters powered by artificial intelligence and digital technologies, created to mimic human-like traits and behaviors on social media platforms. Unlike traditional influencers, who are real people, AI influencers exist purely in the digital world but engage with audiences as if they were real, sharing content, opinions, and lifestyles.
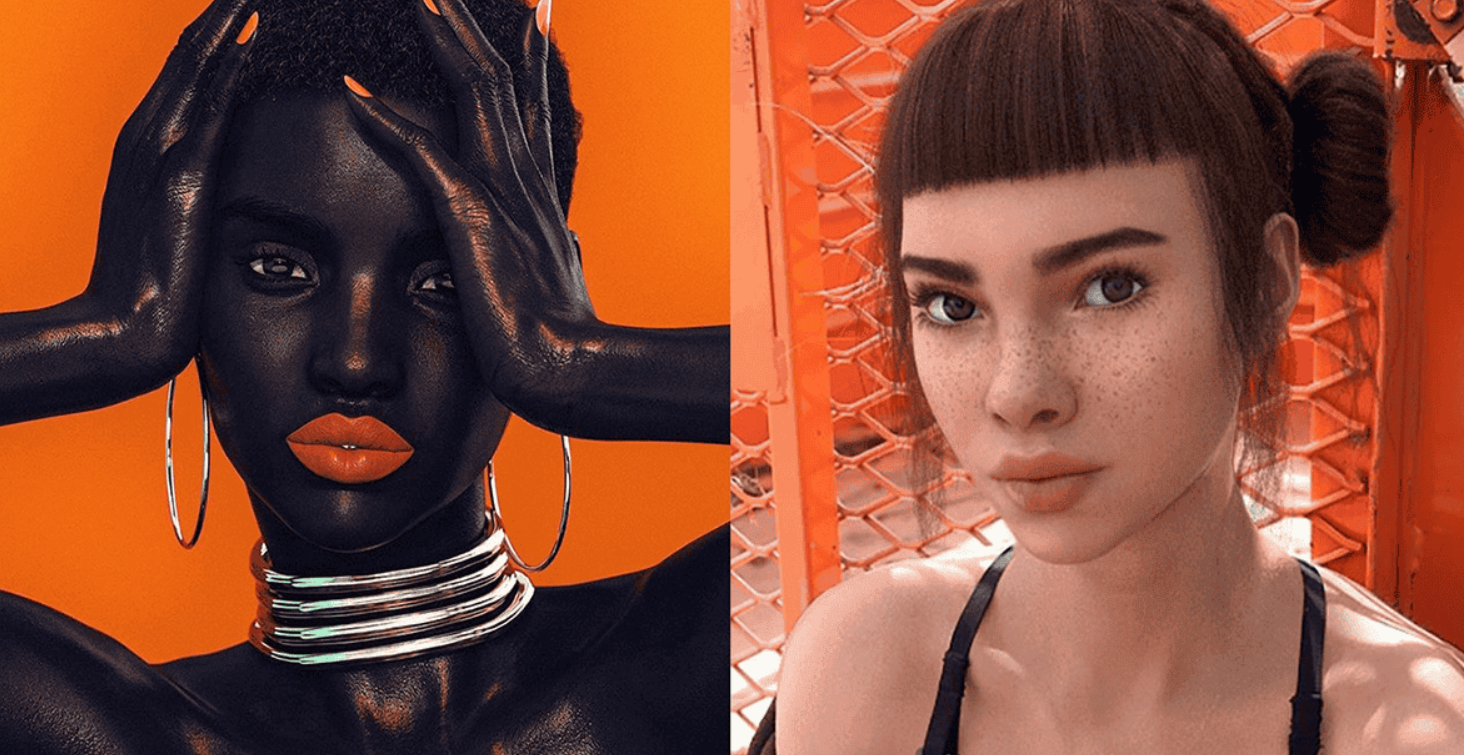

These AI personas are often managed by teams of developers, artists, and marketers who program them to interact with followers, collaborate with brands, and generate content. One of the most famous examples is Lil Miquela, a virtual influencer with millions of followers on Instagram, who collaborates with top fashion brands like Calvin Klein and Prada. Another prominent AI figure is Shudu, a digital model created to reflect the beauty and grace of real-world models, garnering attention from luxury brands and the fashion industry.
These digital personalities appeal to brands because they are highly customizable, don't require breaks, and can maintain a consistent brand image. Additionally, their existence in the digital realm makes them ideal for virtual environments and campaigns, especially in industries such as fashion, beauty, gaming, and entertainment.
The Technology Behind AI Influencers
AI influencers are the product of advanced digital technologies that work together to create lifelike virtual personas. The creation and functioning of these influencers rely on several key technological components, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and 3D modeling software. Together, these technologies enable AI influencers to simulate human behavior, generate content, and engage with audiences in ways that appear remarkably authentic.
1. AI and Machine Learning for Personality Simulation
At the core of AI influencers is machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence that allows systems to learn from data and make decisions. Through machine learning algorithms, AI influencers can simulate human-like behavior by analyzing vast amounts of data from social media interactions, user comments, and trends. This enables them to predict what content will resonate with their audience, how to respond to comments, and what kind of messaging aligns with their digital persona.
AI influencers can also be programmed with specific personality traits. For example, Lil Miquela presents as a socially-conscious influencer, often posting about fashion and human rights issues. These personalities are carefully curated using machine learning models that process and adapt to user feedback, helping AI influencers stay relevant and relatable to their audience.
2. 3D Modeling and Animation for Visual Realism
The visual aspect of AI influencers is often created using 3D modeling and animation software. Tools like Blender, Maya, and Unreal Engine are used to create hyper-realistic avatars that can move, pose, and interact with the environment just like a human model. These virtual avatars are crafted with intricate detail, from their skin textures to their facial expressions, making them appear lifelike in photos and videos.
In some cases, AI influencers use motion capture technology, where the movements of a human actor are captured and transferred onto the digital avatar. This allows for fluid, realistic motion in videos or advertisements. The advancement of 3D rendering software has been key in enabling these digital personas to look so convincing that many users cannot initially distinguish them from real people.
3. Natural Language Processing for Communication
One of the most important aspects of an AI influencer is their ability to engage with followers. NLP is the technology behind this capability. NLP allows AI influencers to generate text, understand context, and respond to comments or messages in a way that feels natural. Chatbots and conversational AI are often integrated into AI influencers, allowing them to reply to direct messages, leave comments, or even create captions that sound like they're written by a real person.
For instance, an AI influencer can be programmed to understand social media slang, humor, and even sarcasm, making their interactions more believable and engaging for followers. NLP also helps maintain consistency in their communication style, ensuring that the AI influencer's "voice" aligns with the persona crafted by their creators.
4. Deep Learning for Image and Video Creation
Deep learning, a more advanced branch of machine learning, plays a significant role in the visual content creation of AI influencers. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a popular deep learning method used to create images and videos. GANs work by training two neural networks against each other: one generates new content, while the other critiques it, improving the quality of the output over time.
This technology is what allows AI influencers to produce highly realistic photos and videos that mimic the style of human influencers. Whether it’s a fashion shoot in a virtual environment or a video of an AI influencer "speaking" to the audience, deep learning algorithms help generate the visual elements that make these digital personas so engaging.
5. Cloud Computing for Real-Time Interactions
The technology that powers AI influencers often relies on cloud computing to handle the massive amounts of data needed for real-time interactions. Cloud-based services provide the processing power to manage everything from responding to user comments to rendering complex 3D environments. This is particularly important for AI influencers that need to engage with followers around the clock, offering a seamless experience regardless of when users interact with them.
Additionally, cloud computing allows the teams behind AI influencers to continuously update their virtual personas, pushing new content, interactions, and personality traits to meet changing trends or user preferences. This ensures that AI influencers can stay current, even as the social media landscape evolves.
The Rise of AI Influencers in Marketing
Why Brands Are Turning to AI Influencers
Brands are increasingly leveraging AI influencers due to several key benefits. One significant advantage is cost-effectiveness. Unlike human influencers, AI influencers don't need travel, accommodation, or other logistical expenses, making them a more budget-friendly option for long-term campaigns. Additionally, they can produce content around the clock without needing breaks, ensuring consistent engagement and interaction with audiences.
AI influencers also have a unique appeal to younger demographics, particularly Gen Z and millennials, who are more tech-savvy and open to digital innovations. These virtual personas often embody the values that resonate with these groups, such as inclusivity, sustainability, and social justice. For instance, Lil Miquela, one of the most well-known AI influencers, frequently incorporates socially conscious messaging into her content, helping brands connect with younger, socially aware audiences.
Successful Case Studies
Using AI in PR allows companies to manage brand perception more effectively by automating media monitoring, crisis management, and audience sentiment analysis. AI influencers have proven their value through several successful campaigns, particularly in industries like fashion, tech, and retail. Below are some notable examples:
1. Lil Miquela and Calvin Klein
One of the most prominent AI influencers, Lil Miquela, has worked with major brands like Calvin Klein and Prada. Her campaign with Calvin Klein, which featured her in an ad alongside model Bella Hadid, generated significant buzz and a sharp increase in social media engagement. Despite some controversy, this collaboration highlighted how AI influencers could spark conversations and elevate brand visibility. Miquela’s human-like appearance and alignment with socially conscious messages make her particularly appealing to Gen Z and millennial audiences.
2. Shudu for Balmain
Shudu, the world’s first digital supermodel, has been an icon in the fashion world. She has collaborated with high-end fashion brands like Balmain. Shudu’s hyper-realistic digital appearance allowed Balmain to experiment with futuristic marketing techniques while attracting widespread attention. This partnership emphasized how AI influencers could enhance a brand’s innovative image.
3. Lu do Magalu and Retail Innovation
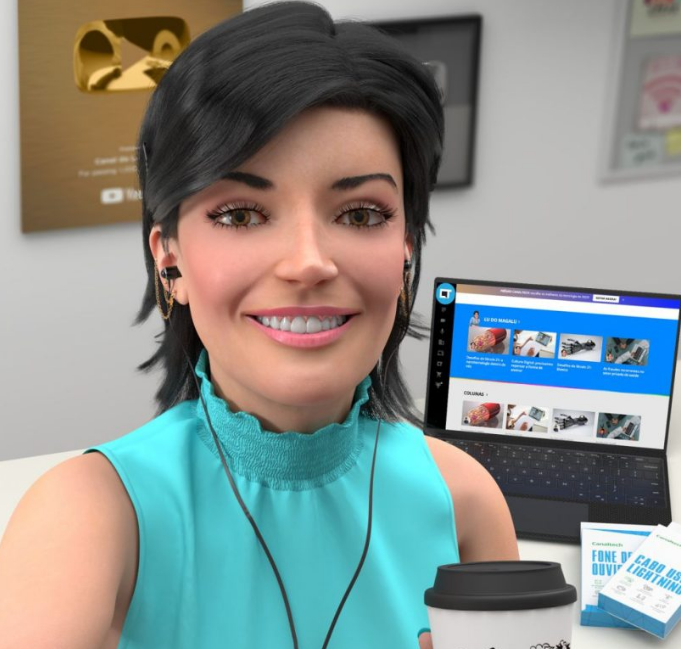

In Brazil, the virtual influencer Lu do Magalu — created by the retailer Magazine Luiza — has become a digital sensation, boasting millions of followers. Lu helps the company engage with its customer base through relatable, consistent content, building a loyal community. Her success has made her a central figure in the retail company’s marketing efforts, showing how AI influencers can thrive beyond the fashion world.
4. Imma and IKEA Japan
In the tech-forward Japanese market, Imma, a virtual influencer, collaborated with IKEA Japan to blend futuristic visuals with minimalist interior design. Her campaigns catered to Japan’s tech-savvy audiences, emphasizing innovative products in an engaging digital environment. Imma’s success showcases how AI influencers can appeal to niche markets.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges of AI Influencers
The rise of AI influencers presents a unique set of ethical challenges that both brands and creators need to navigate carefully. These challenges range from issues of authenticity and representation to data privacy and accountability. Here are some key ethical considerations associated with AI influencers:
1. Authenticity and Trust
One of the biggest challenges is maintaining authenticity. Since AI influencers are digital constructs, they lack the personal experiences and emotional depth of human influencers, which can lead to skepticism among audiences. This artificiality raises questions about whether followers can trust the endorsements or values AI influencers promote, especially in industries that rely on personal experiences, such as wellness and fitness. Brands must strike a balance between innovation and maintaining genuine connections with consumers to avoid losing trust.
2. Unrealistic Beauty Standards
Many AI influencers, especially those in fashion and beauty, perpetuate unrealistic beauty standards. These digital personas, often designed to be physically flawless and perpetually young, contribute to harmful societal expectations around appearance. Critics argue that this reinforces harmful stereotypes and beauty ideals, which can negatively impact mental health, particularly among younger audiences. This issue is compounded when AI influencers, who do not physically exist, promote unattainable aesthetics.
3. Bias and Representation
Another critical ethical issue is the bias embedded in the creation of AI influencers. Since AI models are often built by teams that may not represent the full diversity of the population, biases in race, gender, and culture can be inadvertently reinforced. For instance, concerns arise when white developers create Black AI influencers or male developers create female personas through a biased lens. This lack of representation can perpetuate stereotypes and misrepresent marginalized communities.
4. Data Privacy
AI influencers operate based on vast amounts of data collected from their followers. This raises significant concerns about data privacy. The use of personal data without explicit consent or transparency can lead to breaches of privacy. Brands and developers must ensure that AI influencers are built on secure systems that protect user data and adhere to ethical guidelines regarding data collection and usage.
Many AI consulting companies now provide strategic insights for integrating artificial intelligence into marketing and customer engagement, helping businesses stay competitive in a tech-driven world.
5. Accountability
Finally, the question of accountability looms large when dealing with AI influencers. When an AI influencer makes a mistake or spreads misinformation, it is often unclear who should be held responsible: the brand, the developers, or the AI itself. This ambiguity in accountability can make it challenging to regulate AI influencers and ensure they adhere to ethical standards.
Wrapping Up
AI influencers represent a transformative shift in the landscape of digital marketing, blending technology and creativity in ways that were once unimaginable. They provide brands with a powerful tool to engage with audiences, offering consistency, scalability, and a unique ability to transcend cultural and linguistic barriers. However, as AI influencers become more prominent, it is crucial to address the ethical challenges they present.
Looking ahead, AI influencers are likely to play an even bigger role in the digital marketing space, but their success will depend on how well brands navigate these ethical dilemmas. It is essential for companies to establish transparent and responsible practices, ensuring that AI influencers contribute positively to both marketing and societal standards.